Feature Vector Clustering
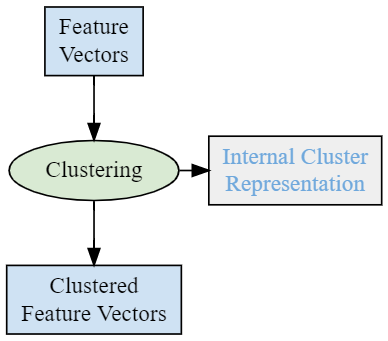
The Feature Vector Clustering microservice creates clusters of its input feature vectors based on similarity.
The microservice implements various clustering algorithms. Its configuration determines which algorithm is in effect in a specific instance. The configuration consists of a general and an algorithm-specific part.
Clustering is based on a similarity measure between feature vectors and clusters. Currently, only trivial algorithms are supported where a single feature vector represents a cluster. The representative feature vector can be the last one belonging to this cluster, or an average of all previous ones.
The input of the microservice can be one or more topics containing feature
vectors or feature vector clusters.
A feature vector cluster is represented by a FeatureVector field and the
number of samples contributing to the cluster. A FeatureVector without
any number of samples is interpreted as if the number of samples were 1.
The microservice maintains a single database for storing feature vector
clusters. The internal cluster representation can be algorithm-specific.
Stored feature vector clusters are first unrealized and may later become realized.
The conditions of realizing a cluster are determined by the Feature Vector
Clustering configuration, see Configuring Feature Vector Clustering.
Registration events are generated for both realized and unrealized clusters
with according value of the is_realized field.
Each change to the database is optionally administered to a compacted Kafka® topic so that the database can be rebuilt from this topic at restart. This method is an alternative to replaying input topics with a window of retention period where data loss may occur in case of a fatal error. See Save and Start from Internal State.
Each registration stream can have an own retention period if configured so. If a cluster is updated, its retention period becomes the maximum of its previous retention period and the retention period set for the stream that is updating the cluster.
Further reading:

 Clustering Process
Clustering Process